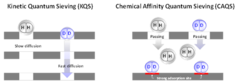
 Hydrogen isotope mixtures can be separated using porous materials by either confinement in small pores i.e. “Kinetic Quantum Sieving” or by strong adsorption sites i.e. “Chemical Affinity Quantum Sieving”. MOFs are excellent candidates for studying these quantum effects due to their well-defined, tunable pore structure and the possibility to introduce strong adsorption sites directly into the framework structure.
Hydrogen isotope mixtures can be separated using porous materials by either confinement in small pores i.e. “Kinetic Quantum Sieving” or by strong adsorption sites i.e. “Chemical Affinity Quantum Sieving”. MOFs are excellent candidates for studying these quantum effects due to their well-defined, tunable pore structure and the possibility to introduce strong adsorption sites directly into the framework structure.
