Principle of Scanning X-ray Microscopy
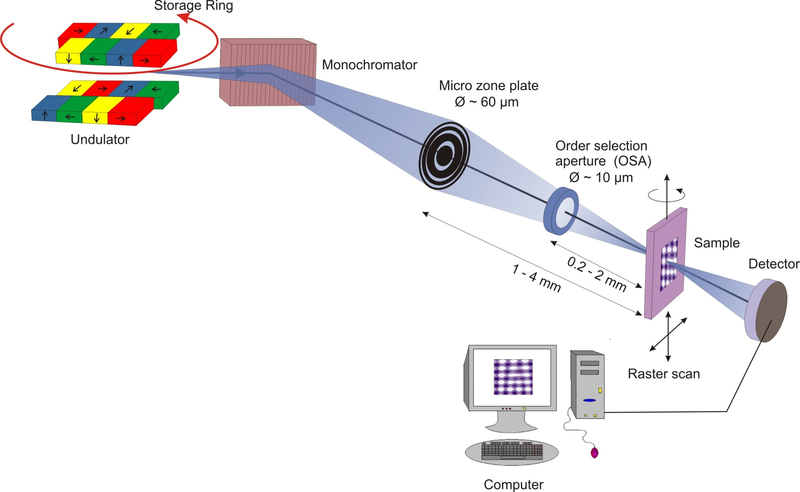 X-rays emitted from an undulator as insertion device in an electron (or positron) storage ring is monochromatized and focused onto the sample by a zone plate, whereby the selected order of diffraction is selected by the OSA ring. The sample is raster scanned and the transmitted intensity monitored by a x-ray sensitive detector (i.e. avalanche diode or x-ray sensitive CCD camera)
X-rays emitted from an undulator as insertion device in an electron (or positron) storage ring is monochromatized and focused onto the sample by a zone plate, whereby the selected order of diffraction is selected by the OSA ring. The sample is raster scanned and the transmitted intensity monitored by a x-ray sensitive detector (i.e. avalanche diode or x-ray sensitive CCD camera)
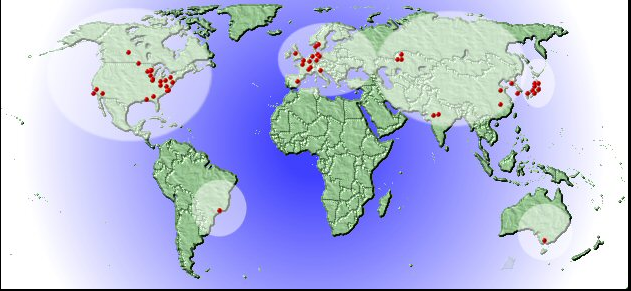 About 50 storage rings world wide provide beam time 7 centers (BESSY, Berlin, NSLS, Brookhaven, ALS, Berkeley; CLS, Kanada; PSI, Schweiz; Elletra, Italien; SSL, Shanghai) run a scanning x-ray microscopy beamline.
About 50 storage rings world wide provide beam time 7 centers (BESSY, Berlin, NSLS, Brookhaven, ALS, Berkeley; CLS, Kanada; PSI, Schweiz; Elletra, Italien; SSL, Shanghai) run a scanning x-ray microscopy beamline.
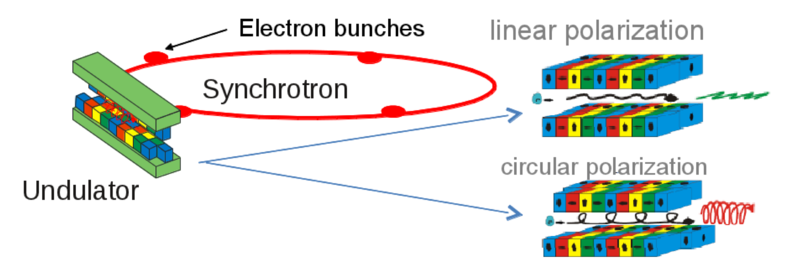
Polarization and time structure of synchrotron radiation
With an undulator the x-ray polarization can be easily varied by adjusting the magnet structure.
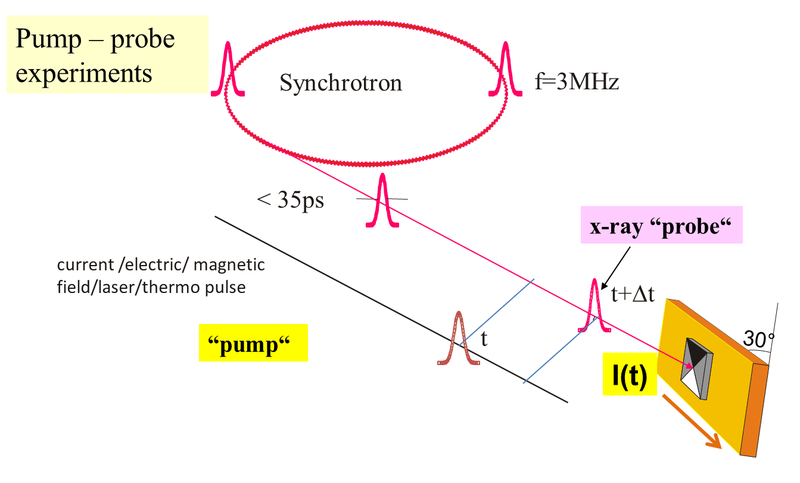
The time structure of the synchrotron radiation (typically flashes of 35 ps pulse widths and 2 ns distance) can be easily be used for pump probe experiments.