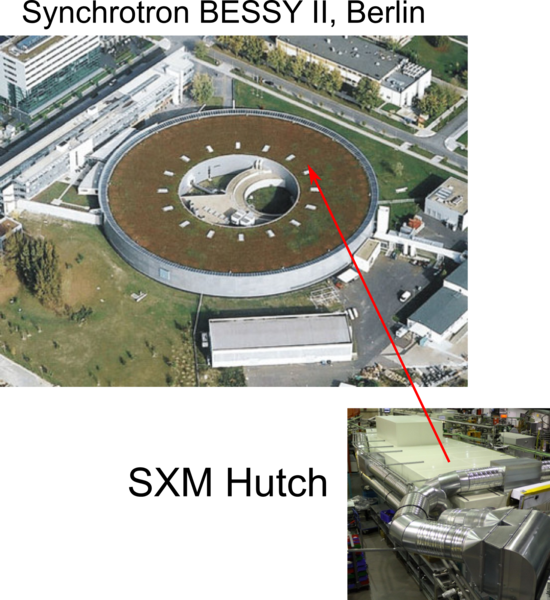
MAXYMUS, our SXM at BESSY
Since 2011 the endstation MAXYMUS ( MAgnetic X-raY Microscope with UHV Spectroscopy) operated by the MPI-IS is open for users.

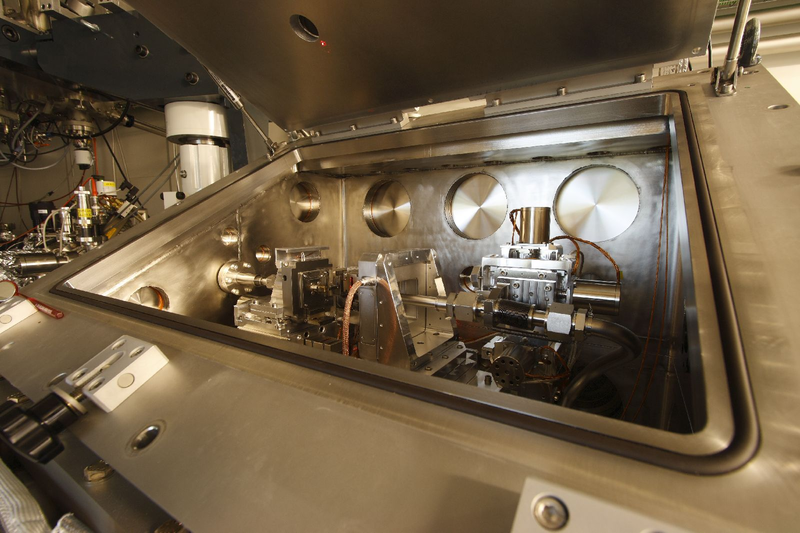
A view into the microscope MAXYMUS
 Properties:
Properties:
- UHV conditions 10-9 mbar
- Zone plate scanning mode
- Goniometer for tomography 360°
- Variable magnetic fields up to 0.4 T
- Wide temperature range 80 – 500 K
- Photocurrent measurements for nontransparent samples and surfaces
MAXYMUS in operating conditions
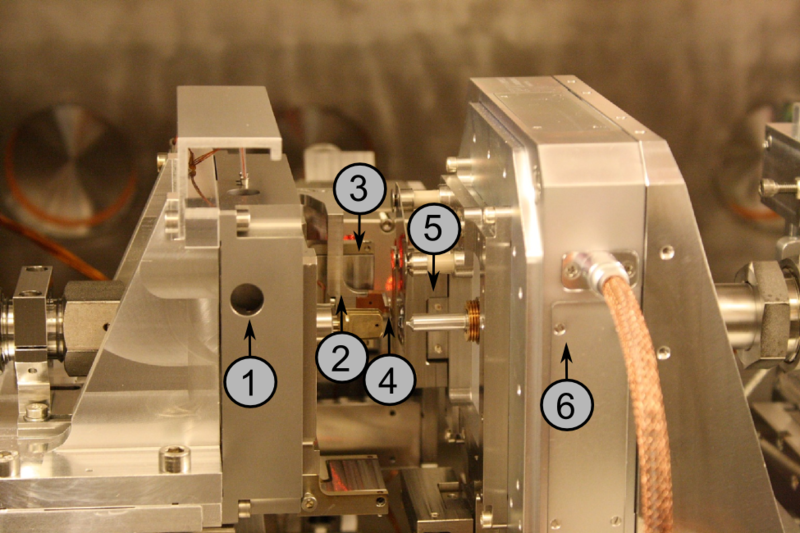 Zone Plate Piezo Stage
Zone Plate Piezo Stage- Zone Plate Holder
- Order Separating Aperture
- Sample
- Photomultiplier
- Sample Piezo Stage
Soft X-ray microscopy (SXM)
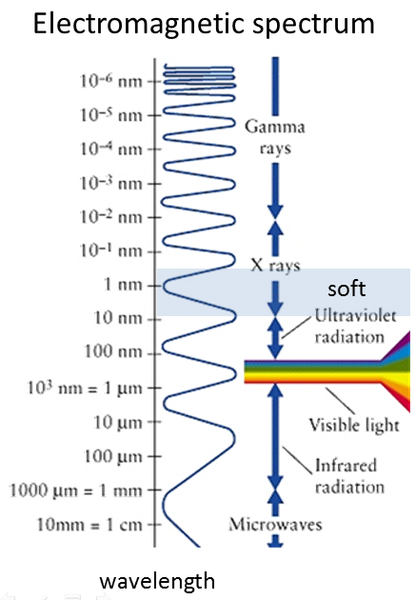 .. uses electromagnetic radiation of 240 to 1.800 eV with wave lengths in the order of 7 nm to 0.7 nm, defining the physical limit of resolution.
.. uses electromagnetic radiation of 240 to 1.800 eV with wave lengths in the order of 7 nm to 0.7 nm, defining the physical limit of resolution.
... was developed in the 70ties by the group of Prof. Schmahl in Göttingen and is a powerful tool to image structures of solids by using high brilliant synchrotron radiation. In combination with spectroscopic methods it provides element specific information on the density distribution of local chemical, electronic and magnetic structure of solids.
... offers new routes to address a variety of static and dynamic issues in modern solid state science including material science, physics, chemistry and biology due to the unique simultaneous combination of important properties:
- High penetration depths of 100 nm to some µm
- High resolution down to 9 nm (best case)
- High temporal resolution down to 10 psec
- Significant chemical sensitivity Large magnetic cross sections
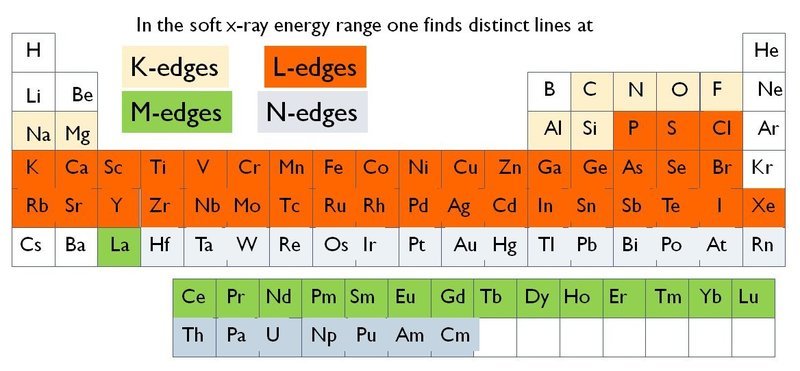
In the soft x-ray range nearly any element exhibit a characteric absorption edge.
Principle of Scanning X-ray Microscopy
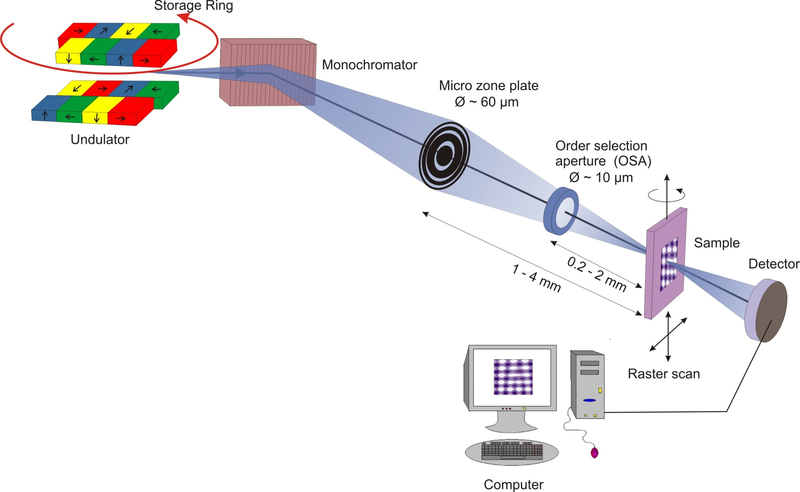 X-rays emitted from an undulator as insertion device in an electron (or positron) storage ring is monochromatized and focused onto the sample by a zone plate, whereby the selected order of diffraction is selected by the OSA ring. The sample is raster scanned and the transmitted intensity monitored by a x-ray sensitive detector (i.e. avalanche diode or x-ray sensitive CCD camera)
X-rays emitted from an undulator as insertion device in an electron (or positron) storage ring is monochromatized and focused onto the sample by a zone plate, whereby the selected order of diffraction is selected by the OSA ring. The sample is raster scanned and the transmitted intensity monitored by a x-ray sensitive detector (i.e. avalanche diode or x-ray sensitive CCD camera)
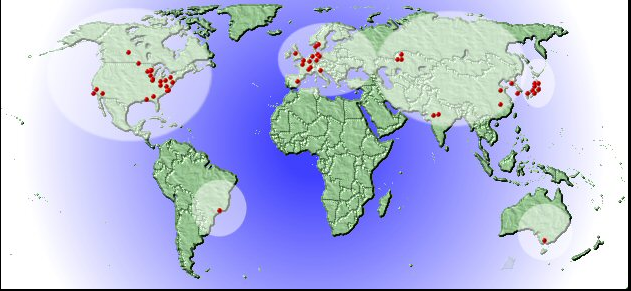 About 50 storage rings world wide provide beam time 7 centers (BESSY, Berlin, NSLS, Brookhaven, ALS, Berkeley; CLS, Kanada; PSI, Schweiz; Elletra, Italien; SSL, Shanghai) run a scanning x-ray microscopy beamline.
About 50 storage rings world wide provide beam time 7 centers (BESSY, Berlin, NSLS, Brookhaven, ALS, Berkeley; CLS, Kanada; PSI, Schweiz; Elletra, Italien; SSL, Shanghai) run a scanning x-ray microscopy beamline.
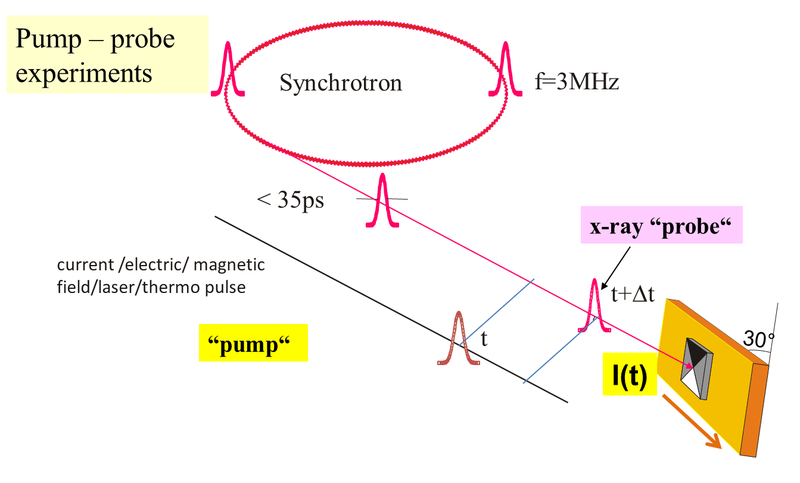
Polarization and time structure of synchrotron radiation
With an undulator the x-ray polarization can be easily varied by adjusting the magnet structure.
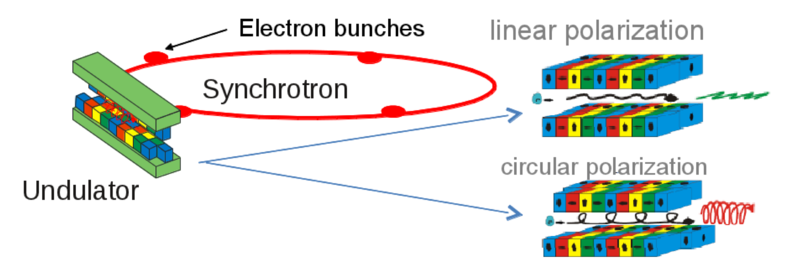
The time structure of the synchrotron radiation (typically flashes of 35 ps pulse widths and 2 ns distance) can be easily be used for pump probe experiments.